Reshaping of the Music Industry
A Data-Driven Look at the Digital Revolution
A Data-Driven Look at the Digital Revolution
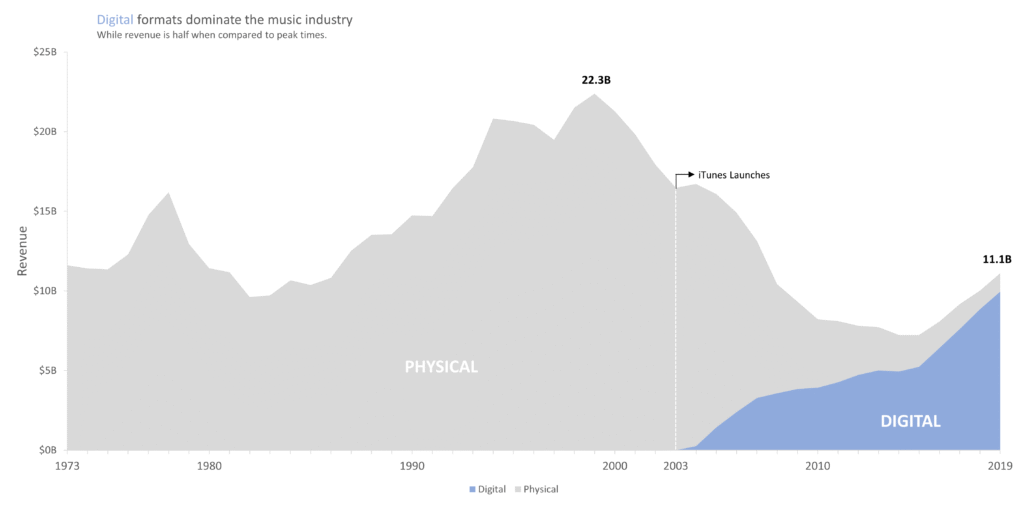
In 2003, Apple launched iTunes a platform that would dramatically alter the course of the music industry. With one click, users could purchase individual songs, breaking away from the traditional album model and signaling the start of a new era. In this blog post, In this analysis conducted using revenue data from the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA), illustrating how the introduction of iTunes and the rise of digital formats forever changed how music is sold and consumed.
The Dataset
The dataset used for this analysis spans multiple years of U.S. music industry revenue, broken down by format. It includes figures for physical media (CDs, vinyl, cassettes), digital downloads, and streaming. The data provides a view of how consumer preferences and revenue streams have evolved, particularly before and after 2003 the year iTunes entered the market.
Tools and Methodology
Using Microsoft Excel, I imported and cleaned the dataset, then calculated several key metrics:
- Total annual revenue to understand the industry’s overall health.
- Revenue by format to distinguish between physical and digital trends.
- Year-over-year growth rates to identify momentum shifts.
- Proportional shares of each format relative to total revenue.
Key Insights
The data clearly marks 2003 as a pivotal year. Prior to iTunes, CD sales were the industry’s bread and butter. But after iTunes launched, digital downloads rapidly gained traction. By 2005, download revenue was growing exponentially, signaling consumer appetite for à la carte song purchases. From the mid-2000s onward, physical format revenue fell steadily. Even though vinyl made a modest comeback in later years, it couldn’t offset the broader collapse in CD sales. Meanwhile, digital formats picked up the slack—first downloads, then streaming.
Another important trend emerged around 2015: streaming began to overtake digital downloads. Services like Spotify and Apple Music shifted the revenue model once again—this time from ownership to access. The data shows streaming becoming the dominant source of music revenue, reflecting a major behavioral change in how people engage with music.
Despite the downturn in physical sales, the industry eventually began to recover, thanks largely to innovation. The digital transformation brought about by iTunes was only the first step. Streaming completed the shift, and by the late 2010s, total revenue had stabilized and even started to grow again.
This analysis shows how the launch of iTunes catalyzed a decades-long transformation in the music industry. While physical formats continue to exist in niche markets, the industry’s future is undoubtedly digital. Tools like Microsoft Excel make it possible to uncover and visualize these macroeconomic shifts, telling a powerful story about adaptation, innovation, and the ever-changing relationship between technology and consumer behavior. Whether you’re a music enthusiast, data analyst, or just curious about the power of data storytelling, this case study is a reminder that behind every trend is a set of numbers waiting to be explored.